We present the new surgical technique Barbed Snore Surgery, his main features and the current state of the art.
Upper airway collapse in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) often has a multi-level etiology that may involve the retro-palatal and/or retro-basilingual and/or laryngeal districts; the collapse of both the uvulo-palatal complex and the lateral pharyngeal walls (LPW) can be revealed by means of pre-operative drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) in many patients with OSAS due to retro-palatal obstruction.
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) is still one of the most widely used procedures for the surgical treatment of snoring and OSAS due to retro-palatal obstruction, but long-term side-effects such as velo-pharyngeal insufficiency, dysphagia, persistent dryness, a globus sensation, voice changes, and nasopharyngeal stenosis are described in up to 58% of patients, and the success rate is no more than 40-60%.
The recently suggested importance of pharyngeal muscular walls in the pathogenesis of retro-palatal OSAS is supported by the encouraging results obtained using the tailored surgical techniques proposed by Cahali and Pang-Tucker Woodson, which have the aim of reducing LPW lateral pharyngeal walls collapsibility by sectioning and relocating the palato-pharyngeal muscle rather than ablating the redundant palato-pharyngeal soft tissue.
1 The BSS – Barbed Snore Surgery
The Barbed Snore Surgery has been developed within the Foundation IRCCS Cà Granda Maggiore Policlinico Hospital of Milan (Italy) in the period between 2008 and 2015 from an idea of Prof. Mario Mantovani.

This new technique, which was later developed in collaboration with the other team in Italy (e.g. Dr. Salamanca in Humanitas – PioX), has been disseminated through scientific papers listed in PubMed, Courses and Conferences, both nationally and internationally.
In 2008 the “Roman blinds technique” (RBT) was introduced, a new surgical approach for the treatment of retro-palatal collapse and vibration in patients with snoring and mild OSAS. This technique was based on Tonnard’s short-scar face lift technique. It consists of stably suspending threads inserted through the fibro-muscular soft palate tissue and LPW lateral pharyngeal walls in such a way that they lift and stiffen the excessively collapsing structures by acting like a Roman blind.
We subsequently enhanced the RBT “Roman blinds technique” in 2011 by introducing the use of “barbed sutures” to suspend the oral and pharyngeal tissue with the aim of improving the biological thread/tissue interaction and eliminating the need for knotting and consequent knot extrusion [17]. This “barbed Roman blinds technique” (BRBT) is characterized by three innovative principles:
- the complete preservation of the oropharyngeal fibro-muscular structures;
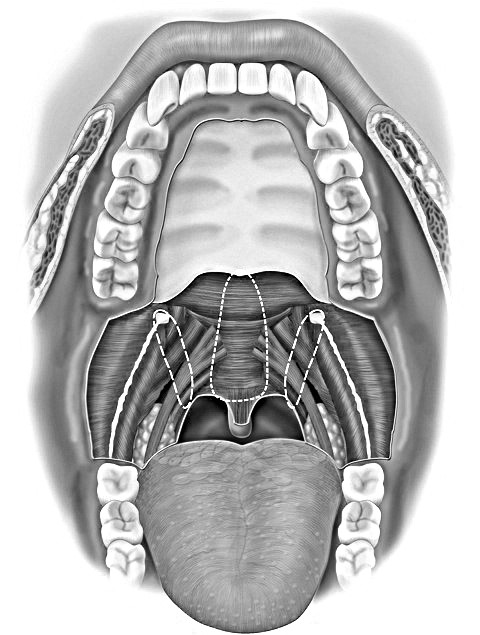
- the identification of specific fibro-osseous holds as suspension points (i.e.: the posterior nasal spine, the hamuli pterygoidei, and the pterygo-mandibular raphes);
- the use of knotless barbed sutures to stabilize the fibro-muscular structure of the soft palate and lateral pharyngeal walls at the suspension points.
BSS includes the BRBT, the BAPh (barbed anterior pharyngoplasty), Alianza (BRBT + anterior pharyngolasty) and BLPh (barbed lateral pharyngoplasty). Each BSS technique has got specific indications on the basis of the results of the DISE (drug-induced sleep endoscopy).
All the BSS procedures creates a tensile structure, interposed between fixed structures (bone and fibrous) and soft tissue (muscle and mucous membranes), with the intent to transfer to the latter the prerogatives of rigidity of the first preventing that during sleep, when the component loses muscle tone, the pharyngeal walls from collapsing in the inspiratory phase, giving rise to the sleep-disordered breathing, snoring and apnea. This tensile structure intratissutal is realized with special self-locking threads, referred to as “Barbed Sutures”, which have the prerogative to act without need for knotting.
No one had ever previously thought to use in this anatomical region such extraordinary suture material. Another important advantage of the new technique, which makes it completely innovative with respect to the previous ones, consists in the fact that do not provide for any section or removal of muscular tissue, thus respecting fully the complex functions of this delicate district of the human body. Barbed wires used are those made of absorbable material, polydioxanone, and therefore destined to disappear altogether in about six months, leaving the fibrous scars, they have created, the task of maintaining over time the results achieved by the intervention.
In conclusion, the main advantages of the new technique of BSS are three:
- Lack of section and resection of fibrous tissue or muscle at the palatal and oropharyngeal: Thanks to this principle, the technique acquires the prerogative to be reversible during the first three / four weeks (before that stabilizes the fibrous scar tissue produced by the manipulations), repeatable, well tolerated and respectful of basic and complex functions that take place in within this section of the human body (it is enough just to remember swallowing and phonation).
- Optimal interaction between cells and barbed sutures: Not requiring be knotted these special threads not concentrated in a single point, that is, in the node, all the force necessary to obtain the approach of the tissues, but the share in countless points, e. at the level of each “beard”: thanks to this prerogative can be avoided ischemic damage to tissues of the load included in the node and tested with obvious advantages in terms of tolerability, of speed of healing and reduction of complications in the processes of scar repair.
- Personalization ‘of the technique in accordance with the needs of each patient:
Contrary to what occurs for most of the other techniques, the surgeon technique that uses the BSS with self-locking thread has the possibility of diversifying the intervention according to the needs of each individual patient, from time to time determined by its anatomical conditions and by evidence of the DISE, the fundamental preoperative diagnostic test, which allows you to see directly into the patient asleep with drugs, where and how to realize the inspiratory collapse of sleep inside of his upper airway. The occurrence of respiratory failure nasal (nose deformity or deviation from-septal, turbinate hypertrophy or malformation for example) or laryngeal obstructive phenomena (genesis or epiglottis arytenoid for example) in a patient candidate BSS require a dedicated surgical planning that, depending on the case, it may provide one or more subsequent sessions.
2 Description of surgical in the form of BSS base named “BRBT – Barbed Roman Blinds Technique” and that associated with front pharyngoplasty called “Alianza”
The interventions both begin by induction of general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation followed by the placement of a self-retaining retractors tongue depressors (the type Boyle-Davis or similar) in order to obtain adequate exposure of the oropharyngeal cavity.
In the first phase is expected exposure of the muscle formations contained in the tonsillar lodge, i.e. muscles and palatoglossal palatofaringeo, contained respectively in the anterior and posterior tonsillar pillar; as the case this phase involves the removal of the palatine tonsils (tonsillectomy) or simply removing the mucus lining the tonsillar lodge of patients already exposed to previous tonsillectomy. Only in very rare cases, as for example in the presence of tonsils of small size and of collapse retropalatale mainly anterior-posterior, it is possible to omit this time.
ALIANZA. Where is programmed association of a front palate plastic is at this point carried out the removal of a crescent of mucosa and submucosa (with the minor salivary glands attached) from the ventral side of the soft palate, just above the uvula base, so as to expose the underlying muscular plane. As we will see below the closure of this modest loss of substance it will be realized with the same thread and the same steps provided for by the basic technique, “BRBT” of the BSS.
The next phases of the operation, the same for both forms, provide accurate control of bleeding followed by ‘identification submucosa rigid structures on either side of the oropharynx (nasal spine back, hooks pterygoid, Rafi pterigomandibolari) and then to the actual phase stress-structural that is realized with a suture thread self-locking, or Barbed Sutures, of the bidirectional type, i.e. provided with two needles, one for each of its ends. The wire, caliber 0 and composed of material to slow resorption (polydioxanone), has a length of 24 or 36 cm for each half and is mounted on needles cylindrical not sharp.
The first needle, for example, the right, is then inserted through the palatal mucosa, one centimeter before the posterior nasal spine, and then pushed through the periosteum, the palatal aponeurosis and the muscles of the soft palate up to leak out to the right side of the base uvula. At this point it slips off the entire right half of the wire until it reaches the stop point (indicative of the entrance into the tissues of the left half of the wire, which can no longer move because of the barbs oriented in the opposite direction). He reintroduces the needle through the hole mucous which was leaking because surrounds one or two times, staying strictly in the submucosal plane, the medial end of the muscles and then goes back palatoglossal palatofaringeo and through the muscles palate until the hook pterygoid right and Pierce finally to escape the overlying mucosa in the mouth. At this point it is sufficient to apply tension to the wire to get the anterior rotation and the stiffening of the emipalato springs right. The same maneuver is sufficient to obtain the combination of the wound edges lunate produced by any pharyngoplasty front associated. We then proceed to re-insert the needle through the same hole from which he had escaped to push it down, keeping it strictly submucosal, embracing the raphe pterygo-jaw with a spiral course along its upper two-thirds; at this point the needle is brought out in the mouth and the wire gently put under tension by pulling the full right half up to the stop point.
It then reintroduces the needle through the same hole from which he had escaped and then, leading him in a latero-medial and horizontally across the bottom of the tonsillar lodge, it is made to reach and embrace orthogonally once or twice palate pharyngeal muscle: Mass live wire will move anterolateral muscle in the same direction raphe pterygo mandibular allowing you get a significant stiffening of this portion oropharyngeal. The maneuver can be repeated, as needed, several times and at various levels to achieve the results desired functional and programmed based on feedback preliminary diagnostic. Once this phase of muscle movement is back with the needle in the region of the hook pterygoid and from here, in the intervention “base” called BRBT or Barbed Roman Blinds Technique, completes the way of the right half of the bezel away from the wire same which began its journey, i.e. at the level of the posterior nasal spine.
ALIANZA. In cases in which had been removed, a crescent of the mucosa and submucosa palatal to realize a front pharyngoplasty the surgical procedure requires that the surgeon grasps with the Holders the right needle, which protrudes from the oral mucosa to the height of the hook pterygoid, and then direct it through the thickness of the soft palate to the right edge of the front edge of the loss of substance lunate then pack a suture intra-submucosa continues to bridge between the two edges of the wound lunate in order to obtain the hermetic seal throughout its length before escape again from the oral mucosa at the level of the hook pterygoid left.
In both forms of BSS described it is envisaged that, once completed the way of the right half of the wire, move to the contralateral left specularly repeating the same path runs to the right. Once this is done it just has to control the hemostasis and cut both wires exactly at the point of exit from the oral mucosa, respectively at the level of the nasal spine in the back of the case and of the hook BRBT pterygoid for ALIANZA.
From the above description it appears evident that this surgical approach allows a considerable freedom of choice to the operator allowing him to modulate in a completely custom action of the barbed wire in breast tissue palatal and pharyngeal, so as to create an intervention “measure” for each patient. Postoperatively, the patient will have to respect the rules of anti-infective prophylaxis with oral rinses with antiseptic mouthwash (for example based on chlorhexidine), taking oral antibiotics and also must observe a diet warm and soft for at least a week. They will also be programmed postoperative controls periodicals, in one to two weeks and then three and six months.
The evaluation of the results will be made objectively by polysomnography examination to be performed at 6 months.
It should be remembered that the tissue changes created by the intervention (with the exception of the removal of tonsillectomy and lunate of palatal mucosa and submucosa) are potentially reversible within the first three to four weeks post-operative, that is, until the intratissutal fibro-cicatricial processes caused by surgical manipulations have not been completed.
Not infrequently in the course of the healing process of wounds oropharyngeal and reabsorption of the suture material (more specifically during the first three to four months postoperative) can be noted barbed wire portions protruding through the oral mucosa which, in addition to become visible in the oral cavity, in some cases can be annoying for the patient: in these cases to solve the small drawback is sufficient that the doctor reference that follows the patient grasp firmly with a clamp the exposed wire portion, and then the sections with a scissor exactly in the point where they exit from the buccal mucosa.
2.1 Description of results
BSS has been and continues to be the subject of clinical trials conducted at hospitals where it is already applied. Preliminary data relating to the results obtained in the period between 2011 and 2014 in 147 adult patients (aged between 28 and 67 years old), with mean follow-up of 14 months, all underwent preoperative DISE and controlled polysomnography at 6-12 months after the intervention, they are the following:
- 80% success rate in 63 simple snorers
- 85% in 84 patients treated for mild to moderate OSAHS.
In both groups, the only major complication, bleeding tonsil postoperative was observed only in cases that have need of tonsillectomy, with an incidence of 4.6% in simple snorers and to 5.9% in OSAHS.
The patients treated to date are of several hundred in different centers and according to the different techniques.
3 BSS next steps
The team of Prof. Mantovani ongoing further development of the BSS technique that should allow significant extension to other cases than today treatable. These developments are down been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fondazione Cà Granda IRCCS Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico of Milan and the first results are expected to be achieved in 2016.
4 Scientific publications
The Barbed Snore Surgery has been the subject of following scientific publications:
- Mantovani M, Minetti A, Torretta S, Pincherle A, Tassone G, Pignataro L. : The velo-uvulo-pharyngeal lift or “Roman Blinds” Technique for treatment of snoring: a preliminary report, Acta Otorhinolaryngol ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/
- Mantovani M, Minetti A, Torretta S, Pincherle A, Tassone G, Pignataro L. : The “Barbed Roman Blinds” technique: a step forward. Acta Otorhinolaryngol ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23853404
- Salamanca F, Costantini F, Mantovani M, Bianchi A, Amaina T, Colombo E, Zibordi F. : Barbed Anterior Pharyngoplasty: an evolution of anterior pharyngoplasty. Acta Otorhinolaryngol.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Barbed+Anterior+Pharyngoplasty%3A+an+evolution+of+anterior+pharyngoplasty - Mantovani M, Rinaldi V., Salamanca F., Torretta S., Carioli D., Gaffuri M., Pignataro L. : Should we stop performing Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty? Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25621277 - Claudio Vicini, Ehsan Hendawy, Aldo Campanini, Mohamed Eesa, Ahmed Bahgat, Saleh AlGhamdi, Giuseppe Meccariello, Andrea DeVito, Filippo Montevecchi, Mario Mantovani: Barbed reposition pharyngoplasty (BRP) for OSAHS: a feasibility, safety, efficacy and teachability pilot study ‘‘We are on the giant’s shoulders’’. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2015.10
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Barbed+reposition+pharyngoplasty+%28BRP%29 - Alexander W. Murphey, MD; Shaun A. Nguyen, MD, MA; Colin Fuller, MD, MS; Aimee C. Weber, MA; Marc P. Camilon, BS; M. Boyd Gillespie, MD, MSc: TranQuill sling snoreplasty for snoring; A singlearm pilot study for safety and effectiveness. The Laryngoscope. 11 www.researchgate.net/publication/283502241_TranQuill_sling_snoreplasty_for_snoring_A_single-arm_pilot_study_for_safety_and_effectiveness
- Mantovani Mario, Rinaldi Vittorio, Torretta S, Carioli D, Salamanca F, Pignataro L.: Barbed Roman blinds technique for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: how we do it?, European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2015.12 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26194006
5 Presentations at academic conferences
The new technique of BSS has been the subject of numerous personal communications made by Prof. Mario Mantovani to Courses and National and International Scientific Conferences devoted to the subject since the year 2010, as shown in the following summary list (main events).
2010
- Congresso “Evoluzione della terapia nella roncopatia”, Casa di Cura Pio X, Milan (Italy), Relazione: ”Lifting uvulo-palatale”
2011
- 98° Congresso Nazionale Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria, Udine, Video: ”Lifting velo-uvulo-faringeo (VUF) o tecnica delle tende a pacchetto per il trattamento del russamento: report preliminare”
- XXI Congresso Nazionale A.I.M.S., Certosa di Pavia (Italy),, Relazione:” Lifting velo-uvulo-faringeo (VUF)”
- XI Corso itinerante di Roncochirurgia, Casa di cura Pio X, Milan (Italy), Relazione (invito): “Lifting uvulo-palatale”.
- 5th ISSS INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM “Surgery, Sleep & Breath”, 30-31 March, Venice (Italy), Relazione (invito) :”The Roman Blinds Technique”
2012
- 2° Simposio sui Disordini del Sonno, Relazione (invito): “Lifting uvulo-palatale”
2013
- New Trend in Palate Surgery, Ospedale S. Orsola, Bologna (Italy), 18-19 Marzo, Relazione “Tecnica delle tende a pacchetto”
- International Symposium on Surgical Technique for Snoring and OSAHS: 2013, Roma 4-5 Aprile, Relazione: “Roman blinds Technique”
- 3° Simposio sui disordini del sonno. Bari, Showille, 15-16 Novembre, Relazione: ”Faringoplastica: la tecnica delle tende a pacchetto con fili autobloccanti”
2014
- Roncochirurgia 3D e Barbed Snore Surgery, Casa di Cura S.Pio X di Milano, 21 Marzo, Relazione: ”Barbed Roman Blinds Technique-BRBT”
- American Academy of Otolaryngology-Haed and Neck Surgery Foundation, Orlando (USA) 21-24 Settembre, Poster: ”A new philosophy in Surgical Management of Snoring: Tolerability and Effectiveness of the Barbed Roman Blinds Technique (BRBT)”
- XII Giornata Salicese (Italy), Corso teorico-pratico, Salice Terme 11 Ottobre, Relazione: ”Barbed Snore Surgery nella chirurgia orofaringea dell’OSAS”
- 2015 Corso di formazione continua ed integrata SIO-AIMS EOS-DRS, Bertinoro (Italy) 13-14 Febbraio, Lezione: “Barbed Snore Surgery, BSS”
2015
- Apnea Treatment, Bologna (Italy) 25-26 Maggio, Relazione: “Faringoplastica con fili autobloccanti, Live surgery: effettuazione in diretta di intervento di Alianza
- III Corso Multidisciplinare ECM “La sindrome delle Apnee notturne nell’adulto: presente e futuro”, Rome (Italy) 16 Aprile, Lectio magistralis: “Barbed Snore Surgery”.
- 12th Middle East Update in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Conference, 18-21 Aprile Madinat Conference Center, Dubai, UAE, Lecture “ The Barbed Snore Surgery, BSS”.
- 1st European Advanced Course on Surgical Tecniques for Snoring and OSAHS, Rome, 2-4 December 2015
